Network switches have been an indispensable component in corporate or data center networking. However, faced with the question that what the exact function of switch in networking is, a few people can answer that in a systematic way. In this post, this question is going to be solved.
What Is the Network Switch
The network switch in networking is a small hardware device that can be regarded as a network bridge with multi-ports, centrally addressing communications among all sort of connected devices, like servers, PCs, and access points within one local area network (LAN).

Figure 1: Network Switches in NetWorking
Types of the Network Switches
As shown in the market, there is a wide range of switches in the market. If you want to figure them out, you should bear in mind with clear criteria. With different standards, types of the switch are matched differently. For example, based on the transmitting rapid, you can get subbranches, like fast Ethernet switch, Gigabit Ethernet switch, 10Gigabit switch, etc. When looking at the configuration options, unmanaged switch and managed switch can be found. In this part, the configuration option will be introduced in details.
In networking, an unmanaged switch is used to achieve basic connectivity without any configuration interface or options. Just plug them in, they will work. Mostly, they are preferred in small offices and home offices environment or wherever a few ports are needed.
Comparing with an unmanaged switch, the managed switch, also called smart switches, gives users more flexibility to configure switches as they need. Surely, it brings greater security and targeted networking to users. It supports many management interfaces, like Web UI, CLI, or both. The configuration of VLAN is the common application for a managed switch. For this type, 10gbe switch, 40gbe switch and 100gbe switch are the common choices.

Figure 2: Unmanaged Switch (Left) and Managed Switch (Right)
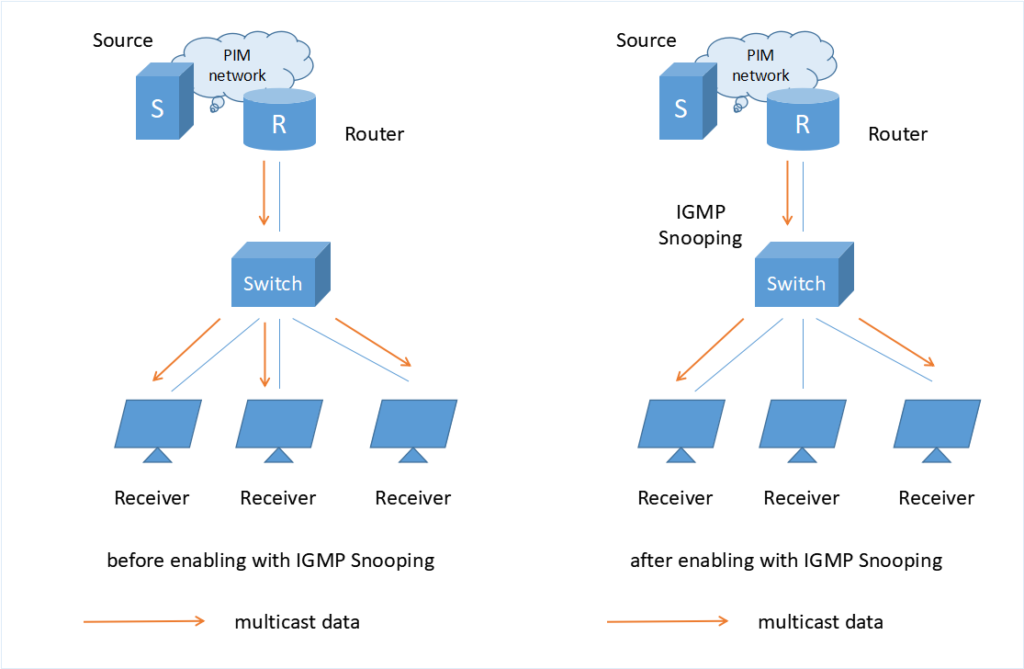
The Function of Switch in Networking
No matter in your home or small offices, the network switch seems to be ubiquitous in network applications. For people outside the industry, you may wonder what the switch function is or what the benefits will the network switch brings about. Here, the main function of switch in networking will be listed below:
- Saving cost. Running cables to industrial Ethernet nodes one by one, it’s a huge cost and even unreliable. Therefore, the switch can be a cost-effective choice in wiring.
- Easy installation. Without the need for the climate controlled enclosure, switch installation will be easier and more convenient.
- Low latency. When the transmission of network packet between the source device and target device has low latency, the time will be saved.
- Eliminating collision. With specified ports of the network switches, the access of the data packet sent by different devices will be spotted faster and targeted transmitted to the matching devices without unnecessary collision.
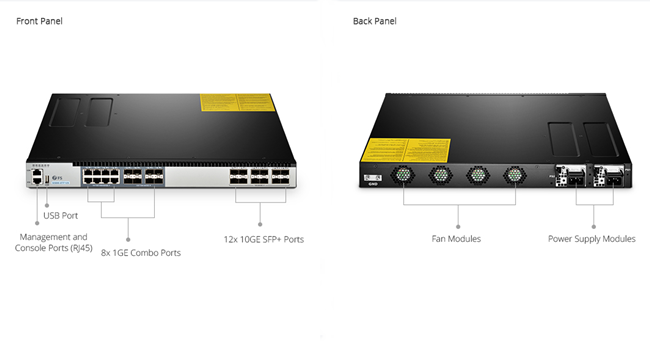
Figure 3: Front and Back Panel Overview of S5800-8TF12S Fully-Managed Switch
Summary
As an essential component in network cabling, the function of switch in networking has been highlighted by many users. In this post, the general function of switch has been introduced. If you want to know more about network switches or solutions for network cabling, you can visit FS.COM for professional guidance.