With the development of science and technology, the demand for large-scale communication construction is increasing. The fiber optic cable industry has developed rapidly, and has formed a complete industrial chain from fiber preform to optical fiber cable. Then, what is fiber optic cable?
Fiber Optic Cable Definition
To get clear what is fiber optic cable, here starts from the fiber optic cable definition. Also known as optical fiber cable, fiber optic cable is a cable-like component that contains one or more optical fibers that used to carry light. Individually coated with plastic layers, the fiber optic components are contained in a protective tubes suitable for the environment in which the cable will be deployed. With the different types, fiber optic cables are used for different applications, such as long distance communication, or to provide high speed data connections between different parts of a building.
Fiber Optic Cable Structure
The basic structure of fiber optic cable consists of three parts: the core, the cladding, and the coating or buffer. Light propagates mainly along the core which is a cylindrical rod of dielectric material that conducts no electricity. Generally made of glass, the core is surrounded by a layer of material called the cladding. Even though light will propagate along the fiber core without the layer of cladding material, the cladding does perform some necessary functions. The cladding layer is made of a dielectric material. Generally made of glass or plastic, cladding performs the following functions: redounding loss of light from the core into the surrounding air, reducing scattering loss at the surface of the core, and preventing the fiber from absorbing surface contaminants.
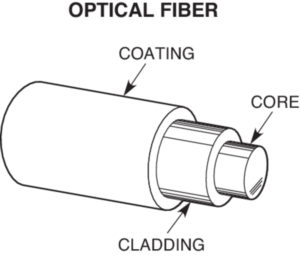
Figure 1: structure of fiber optic cable
Fiber Optic Cable Types
Fiber optic cable types can be commonly divided into single mode and multimode optical fiber. With a diameter of 8.3 to 10 microns, single mode cable is a single stand of glass fiber, which has one mode of transmission. Single mode fiber has a relatively narrower diameter, through which only one mode will propagate typically 1310 or 1550nm. Although carrying higher bandwidth than multimode fiber, it requires a light source with a narrower spectral width. Multimode cable has a little bit bigger diameter, with a common diameters in the 50-to-100 micron range for the light carry component. Then how do we distinguish the single mode and multimode fibers?
The main difference between the multimode and single mode fibers is that the former has a larger diameter (usually the core diameter of the 50 or 62µm), and the typical single mode fiber has the core diameter of 8 and 10µm. The cladding diameter of both is 125µm.
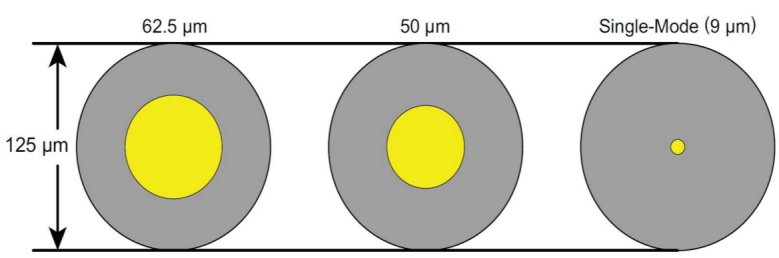
Figure 2: single mode and multimode optical fiber
Both lasers and LED are usually used as light sources. The laser source is much more expensive than the LED light source, because its light can be precisely controlled and has higher power. The light produced by the LED light source is more dispersed (many modes of light), and these light sources are mostly used in multimode optical fiber jumpers. Besides, the laser source which produces near single mode light is usually used in single mode optical fiber jumpers.
Because multimode fiber has larger core size than single mode fiber, it supports multiple transmission modes. In addition, like multimode fiber, the single mode fiber also presents mode dispersion caused by multiple spatial modes, but the mode dispersion of the single mode fiber is less than that of the multimode fiber. For these reasons, the single mode optical fiber has a wider bandwidth than the multimode optical fiber.
According to the TIA-598C standard, for non military purposes, single mode optical fiber adopts yellow outer jacket, and multimode optical fiber adopts orange or aqua outer jacket.
Multimode fiber has higher pulse expansion rate than single mode fiber, which limits the information transmission capacity of multimode optical fiber.
Fiber Optic Cable Advantages and Disadvantages
As we all know, at present, the application of optical fiber in communication can be seen everywhere. What are fiber optic cable advantages and disadvantages?
- Greater Bandwidth – Besides with immunity to electromagnetic interference, fiber optic cables have a much greater bandwidth and are much thinner and lighter than metal cables.
- Larger Capacity – As the most secure medium available for carrying sensitive data, fiber optic cables have larger capacity and greater tensile strength than copper.
- Lower Power Loss – An optical fiber offers low power loss, which allows for longer transmission distances.
- Lower Cost – The raw materials for glass are plentiful, unlike copper which means glass can be made more cheaply than copper.
- Difficult to Splice – The optical fibers are difficult to splice, and there are loss of the light in the fiber due to scattering. They have limited physical arc of cables.
- High Price to Install – The optical fibers are more expensive to install, and they have to be installed by the specialists.
- Can’t Be Curved – Besides, the fiber optic cables can’t be curved, because the fibers can be broken or have transmission losses when wrapped around curves of only a few centimeters radius.
Fiber optic cable has both advantages and disadvantages. However, in the long run, optical fiber will replace copper. Nowadays, widely used, fiber optic cable becomes more popular than before. FS.COM, as the pioneer of optics supplier, provides all kinds of high-quality and reasonable-price optical fiber cables for your option.