Selecting the optimum solution for your cabling infrastructure is vital. Basically there exist two options: fiber and copper. Since both offer some unique benefits and superior data transmission, it is rather hard to decide which one to use. Generally, your choice should depend on your current network, your future networking needs, and your particular application, including bandwidth, distances, environment, and cost. Although in some circumstance copper may be a better choice, in other situations, however, fiber cable obtains much more advantages.

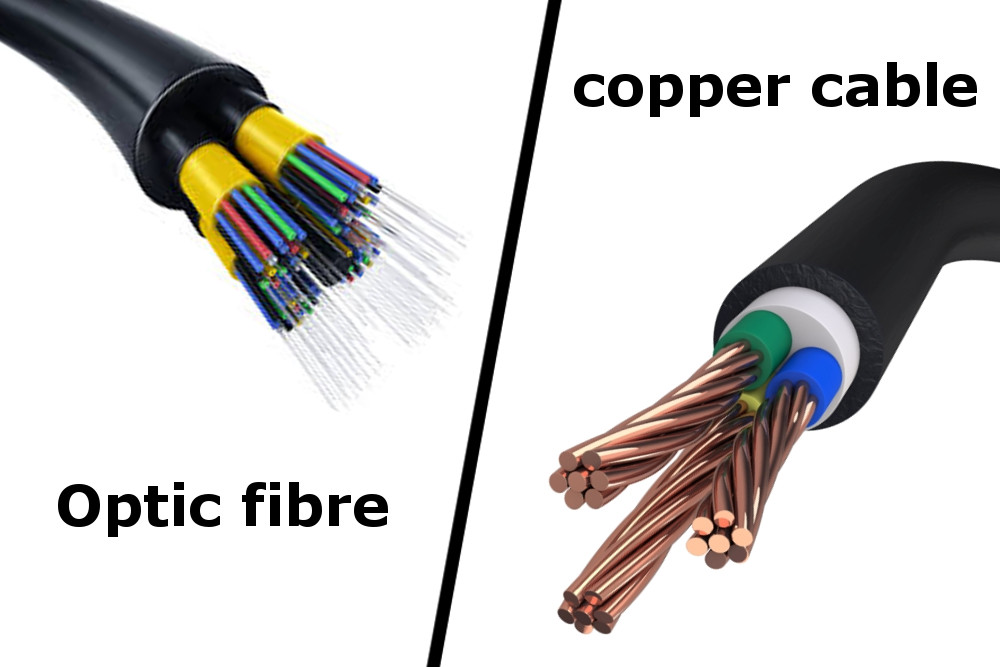
The very first step before you making the choice is to figure out the distinct properties of fiber optic cable and copper cable. To make it clear, we make a comparison here.
Power over Ethernet (PoE)—This offers you many other devices right through the networking cable itself, including power phones, surveillance cameras, Wireless Access Points (WAPs). It means that you don’t have to schedule an electrician in to run power to your surveillance cameras. Another advantage is the ability to have an emergency power supply that will continue powering mission critical devices even if your electricity goes out.
Less expensive electronics—If you are going to take fiber to the workspace, realize that most PC’s come with copper NIC cards. Optical ones will cost you between $100-200 each.
More flexible—TDM environments are built to run on copper infrastructures. Fiber can be used, however the electronics that make it work are expensive.
Fiber cable provides far greater bandwidth than copper and has standardized performance up to 10 Gbps. Keep in mind that fiber speeds are dependent on the type of cable used. Single-mode cable offers far greater distance than either 62.5- or 50-micron multimode cable. In addition, fiber optic cable can carry more information with greater fidelity than copper wire. That’s why telephone and CATV companies are converting to fiber.
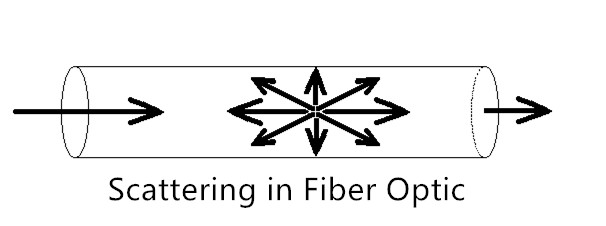
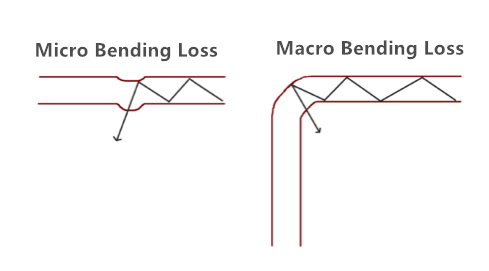
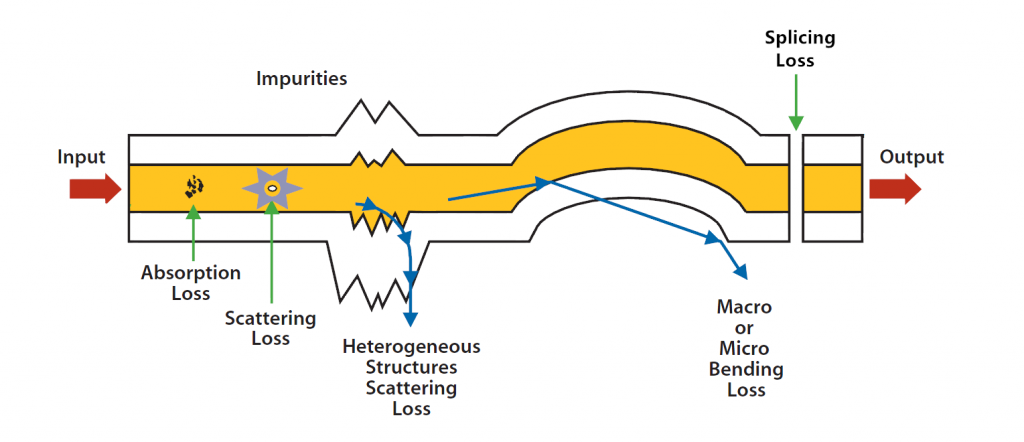
Because the fiber optic signal is made of light, very little signal loss occurs during transmission, and data can move at higher speeds and greater distances. Fiber does not have the 100-meter distance limitation of unshielded twisted pair copper (without a booster). Fiber distances can range from 300 meters to 40 kilometers, depending on the style of cable, wavelength, and network. Fiber cable performs better since fiber signals need less boosting than copper ones do.
Fiber provides extremely reliable data transmission. It’s completely immune to many environmental factors that affect copper cable. The core is made of glass, which is an insulator, so no electric current can flow through. It’s immune to electrometric interference (EMI) and crosstalk, impedance problems, and more. You can run fiber cable next to industrial equipment without worry. Fiber is also less susceptible to temperature fluctuations than copper and can be submerged in water.
Fiber is lightweight, thin, and more durable than copper cable. Meanwhile, fiber optic cable has pulling specifications that are up to 10 times greater than copper cable’s. It’s easier to handle due to its small size, and it takes up much less space in cabling ducts. In addition, fiber is actually easier to test than copper cable.
Media converters make it possible to incorporate fiber into existing networks. The converters extend UTP Ethernet connections over fiber optic cable. Modular patch panel solutions (we’ve discussed before) integrate equipment with 10 Gb, 40 Gb and 100/120 Gb speeds to meet current needs and provide flexibility for future needs. The panels in these solutions accommodate a variety of cassettes for different types of fiber patch cables.

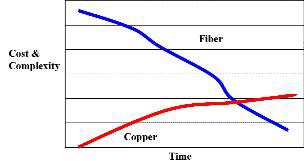
The cost for fiber cable, components, and hardware is decreasing steadily. Installation costs for fiber are higher than copper because of the skill needed for terminations. Although fiber is more expensive than copper in the short run, it may actually be cost-efficient in the long run. Fiber typically costs less to maintain, has much less downtime, and requires less networking hardware. And fiber eliminates the need to re-cable for higher network performance.
Fiber cable enables safer data transmission. It doesn’t radiate signals and is extremely difficult to tap. Once the cable is tapped, it’s very easy to monitor because the cable leaks light, causing the entire system to fail. If an attempt is made to break the physical security of your fiber system, you’ll know it. Fiber networks also enable you to put all your electronics and hardware in one central location, instead of having wiring closets with equipment throughout the building
We have explained the basic differentiator between fiber and copper, and it is rather clear that fiber cable is quickly rising in popularity, and more favored by new cabling installations and upgrades because of the benefits that come along with it. However, do remember that your cabling decisions should better depend on your very specific circumstances.