Standard fiber patch cables are widely discovered in our life, but fiber patch cables also have other special types, such as the mode conditioning cables, fiber loopbacks, etc. These special fiber patch cables are usually used for some particular applications. In this article, we will mainly introduce the basic knowledge of PM (polarization maintaining) patch cables.

In fiber optic industry, polarization maintaining fiber is a single-mode fiber that can maintain a linear polarization light propagation during the whole transmission inside fiber. As long as the light is linearly launched into the fiber, its polarization in the fiber path will not change. PM patch cable is a fiber optic cable consisting of PM fiber and high-quality ceramic fiber optic connectors. With the special polarization maintaining function, PM patch cables have the characteristics of low insertion loss, high extinction ratio, high return loss, excellent changeability over a wide wavelength range and excellent environmental stability and reliability.
PM patch cables have various types according to different classification bases. To choose the right type of PM fiber patch cable, you may consider the following aspects.
Similar to standard fiber optic cables, the common connectors for PM fiber patch cables are LC, SC, FC and ST types. Connectors on both ends of the cable can be identical or different, such as LC-LC or LC-SC connectors. The special part is that connector ends are capped for better protection since the PM connectors are made to be more sophisticated.
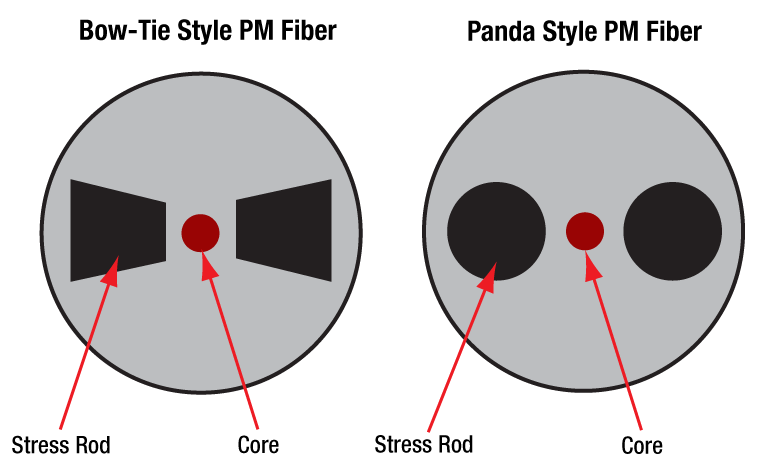
PM fiber patch cables all use the PM fibers. However, PM fibers can be different according to different shapes of the inside rod. This special rod can ensure the linear polarization of input and output light in the fiber. The following picture shows the examples of “Panda” and “Bow-Tie” styles of PM fiber.
With or without cable jacket are both common for PM fiber patch cables. Generally speaking, there are three types of PM cables – 250μm bare fiber PM cable, 900μm loose tube jacket PM cable and 3mm loose tube jacket PM cable.
The standard cable length of PM fiber patch cables is 1 meter. If other lengths are required, the cable is able to be customized to the required lengths as well.
Since PM fibers are typically used to guide linearly polarized light from point to point, PM fibers can be used for many special applications in optical sensors or telecommunications and sensor research. PM fiber patch cables are especially useful for polarization sensitive fiber optical systems where optical light needs to be maintained at a linear state. PM fiber patch cables can be used with other devices like interferometric sensors, integrated optics, fiber amplifiers in high-speed and coherent telecommunications.
As one type of special fiber patch cables, PM patch cables are particularly designed for keeping the polarization of linear optical lights. PM patch cable is definitely a good solution to ensure the high performance of data transmission. FS.COM offers various types of PM patch cables with length customization service. If you are interested in more details, please kindly visit FS.COM or contact us via sales@fs.com.