As more bandwidth and faster data transmission rates over long distances are needed, users have to rely on more fiber optics. But laying more fibers will cost much. So WDM (Wave Division Multiplexing) technology appeared and solved this problem.
WDM is a technology which transmits multiple optical signals on a single fiber by using different wavelengths, or colors, of laser light to carry the different signals. By using bidirectional communications over a single fiber, network users can realize a multiplication effect in their available fiber’s capacity. The effect of expanding the capacity of the network without laying more fibers makes WDM systems so popular. The concept was first published in 1978. At the very beginning, only two signals could be combined by using WDM systems. But now more signals could be handled and transmission rates get faster.
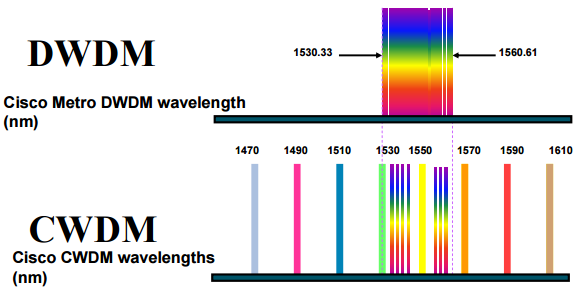
Currently WDM systems are divided into two different types: CWDM (coarse wavelength division multiplexing) and DWDM (dense wavelength division multiplexing). CWDM systems typically have 8 channels with 8 wavelengths separated by 20 nm from 1470 nm to 1610 nm. But the channels could also be increased to 16. Typical DWDM systems use 40 channels and provide wavelengths up to 96 with 0.4nm spacing. The channel spacing decides the call of “coarse” and “dense”. There are many differences between these two systems.
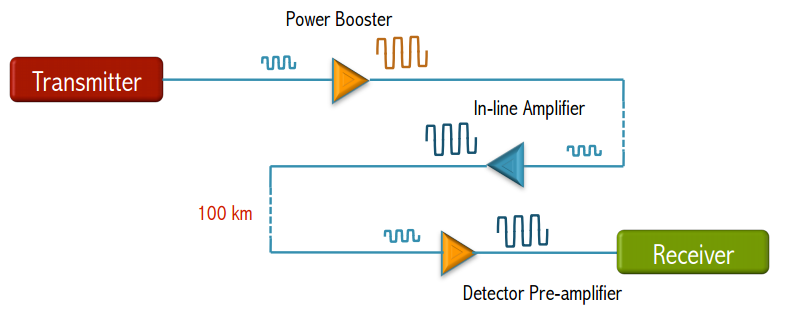
CWDM systems can’t transmit data over distances as long as DWDM system because the wavelengths are not amplified. Usually CWDM can travel somewhere about 100 miles. Therefore CWDM is limited in its functionality over longer distances. While DWDM systems are set for long haul transmission by keeping the wavelengths tightly packed. They can transmit more data over longer distances with less interference than a CWDM system. So it’s suitable for data transmission over long distances.
The power requirements for DWDM are significantly higher. For example, DWDM lasers are temperature-stabilized with Peltier coolers integrated into their module package. The cooler along with associated monitor and control circuitry consumes around 4 W per wavelength. But CWDM uses uncooled laser transmitter and it consumes about 0.5 W of power.
Two main factors like operating and hardware cost cause difference between CWDM and DWDM. The first example has been referred before. CWDM modulation laser is uncooled, but DWDM laser is cooling. Cooling laser using temperature tuning, uncooled laser adopts electronic tuning. The range of temperature distribution is non-uniform in a very wide wavelength, so the temperature tuning is very difficult to realize, which results in high cost. CWDM doesn’t have this problem. Second, for instance, DWDM transceivers are typically four or five times more expensive than CWDM counterparts. That’s mainly because of the lasers. Typical wavelength tolerances for DWDM lasers die are on the order of ±0.1 nm; whereas tolerances for CWDM lasers die are ±2-3 nm. Lower die yields increase the costs of DWDM lasers relative to CWDM lasers. From these two sides, CWDM system is cheaper than DWDM system.
Each kind of WDM system has its advantages and disadvantages. CWDM is very flexible and is good for campus LAN expansion. DWDM has large capacity and is ideal for long distance data transmission. CWDM and DWDM technology continue be to improved. The two have different functions and will complement not replace the other.