The tremendous growth in IP traffic badly influenced the access network capacity. It’s believed that the copper-based access networks can’t provide either the minimum bandwidth or the required transmission distance for delivering services of voice, data, and video programs. Passive optical network (PON) is seemed as a promising and cost-effective way to solve this problem.
PON is a telecommunication network that uses point-to-multipoint fiber to the end-points in which optical splitters are used to enable a single optical fiber to serve multiple end-points. It does not include any electrically powered switching equipment.
There are three distinct devices in the network (as shown in the following picture): the OLT (optical line terminal), the ONUs (optical network units) or ONTs (optical network terminals) and the splitter. Each one has a necessary function in the passive optical network. PON always works under transmission between the OLT and the different ONT’s through optical splitters, which multiplex or demultiplex signals based on their origin and destination.
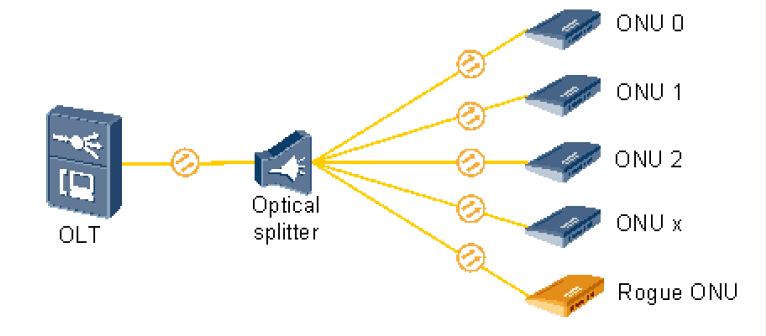
- OLTs are located in provider’s central switching office. This equipment serves as the point of origination for FTTP (Fiber-to-the-Premises) transmissions coming into and out of the national provider’s network. An OLT, is where the PON cards reside.
- ONU converts optical signals transmitted via fiber to electrical signals. These electrical signals are then sent to individual subscribers. ONUs are commonly used in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) or fiber-to-the-curb (FTTC) applications. Using different wavelengths for each service makes it possible to transmit high-speed Internet and video services at the same time. Wavelength multiplexing is performed at the central office and a wavelength demultiplexing mechanism is provided at the customer’s house.
- PON splitter is used to split the fiber optic light into several parts at a certain ratio. For example, a 1X2 50:50 fiber optic splitter will split a fiber optic light beam into two parts, each get 50 percent of the original beam.
There are many advantages given by the use of fiber and the passive elements that compose the network. The following will tell about the advantages of PON.
-
High bandwidth The bandwidth allowed by systems based on PON can reach the 10 Gbps rate down to the user. The need to increase the bandwidth and the speed is another justification for the use of PON.
-
Long distance A PON allows for longer distances between central offices and customer premises. While with the Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) the maximum distance between the central office and the customer is only 18000 feet (approximately 5.5 km), a PON local loop can operate at distances of over 20 km.
-
Low cost On one hand, the cost of passive elements is low. On the other hand, the installation of these PON elements is much more economic. And it avoids operation and maintenance costs, such as absence of falls or maintenance of the network feeds.
Of course PON has some disadvantages. Compared with an active optical network, it has less range. That means subscribers must be geographically closer to the central source of the data. PON also make it difficult to isolate a failure when they occur. However, these disadvantages can not avoid choosing PON as the best possible configuration. Because it saves the cost of deploying PON networks regarding other two configurations (point to point and active optical network). And the flexibility of the network allows the usage of a channel by a large number of users.
