
OSFP stands for Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable, which consists of 8 electrical lanes, running at 50Gb/s each, for a total of the bandwidth of 400Gb/s. This post will give an introduction of 400G OSFP transceiver types, the fiber connections, and some QAs about OSFP.
400G OSFP Transceiver Types
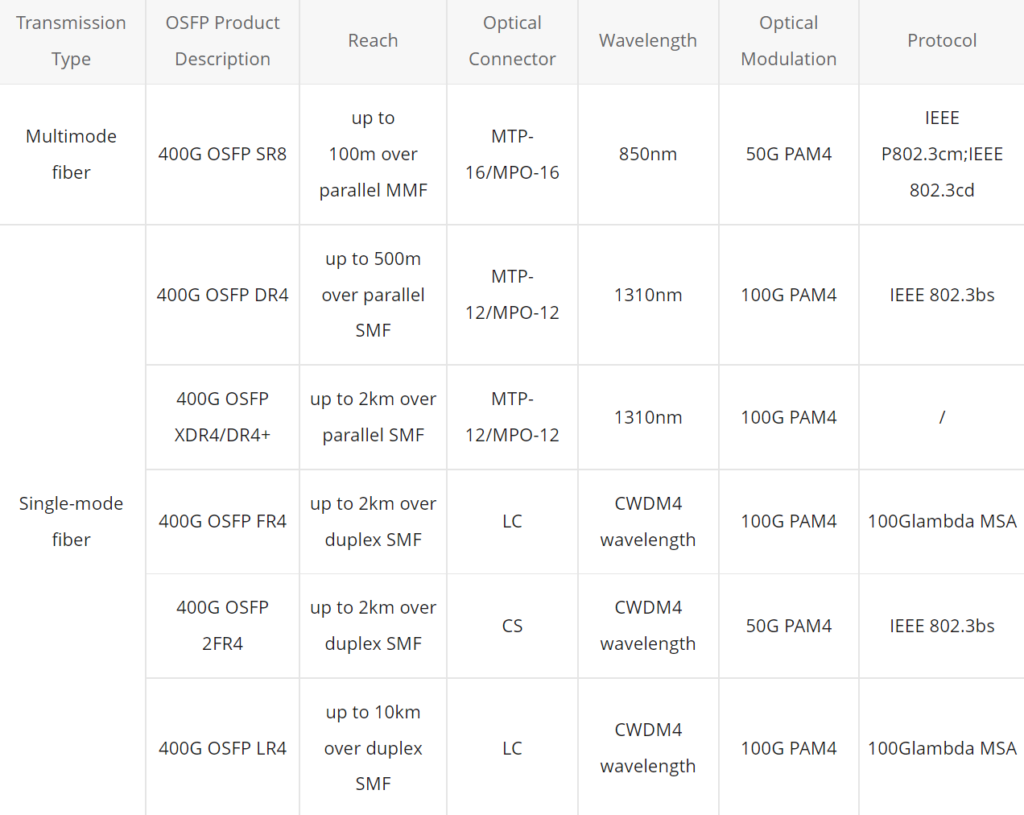
Below lists some current main 400G OSFP transceiver types: OSFP SR8, OSFP DR4, OSFP DR4+, OSFP FR4, OSFP 2*FR4, and OSFP LR4, which summarize OSFP transceiver according to the two transmission types (over multimode fiber and single-mode fiber) they support.
Fibers Connections for 400G OSFP Transceivers
400G OSFP SR8
- Connect a 400G OSFP SR8 transceiver with another 400G OSFP SR8 transceiver over an MTP-16/MPO-16 cable.

- 400G OSFP SR8 to 2× 200G SR4 over MTP-16 to 2× MPO-8 breakout cable.

- 400G OSFP SR8 to 8× 50G SFP via MTP-16 to 8× LC duplex breakout cable with up to 100m.

400G OSFP DR4
- 400G OSFP DR4 to 400G OSFP DR4 over an MTP-12/MPO-12 cable.

- 400G OSFP DR4 to 4× 100G DR4 over MTP-12/MPO-12 to 4× LC duplex breakout cable.

400G OSFP XDR4/DR4+
- 400G OSFP DR4+ to 400G OSFP DR4+ over an MTP-12/MPO-12 cable.

- 400G OSFP DR4+ to 4× 100G DR over MTP-12/MPO-12 to 4× LC duplex breakout cable.

400G OSFP FR4
400G OSFP FR4 to 400G OSFP FR4 over duplex LC cable.

400G OSFP 2FR4
OSFP 2FR4 can break out to 2× 200G and interop with 2× 200G-FR4 QSFP transceivers via 2× CS to 2× LC duplex cable.

400G OSFP Transceivers: Q&A
Q: What does “SR8”, “DR4”, “XDR4”, “FR4”, and “LR4” mean?
A: “SR” refers to short range, and “8” implies there are 8 optical channels. “DR” refers to 500m reach using single-mode fiber, and “4” implies there are 4 optical channels. “XDR4” is short for “eXtended reach DR4”. And “LR” refers to 10km reach using single-mode fiber.
Q: Can I plug an OSFP transceiver module into a QSFP-DD port?
A: No. QSFP-DD and OSFP are totally different form factors. For more information about QSFP-DD transceivers, you can refer to 400G QSFP-DD Transceiver Types Overview. You can use only one kind of form factor in the corresponding system. E.g., if you have an OSFP system, OSFP transceivers and cables must be used.
Q: Can I plug a 100G QSFP28 module into an OSFP port?
A: Yes. A QSFP28 module can be inserted into an OSFP port but with an adapter. When using a QSFP28 module in an OSFP port, the OSFP port must be configured for a data rate of 100G instead of 400G.
Q: What other breakout options are possible apart from using OSFP modules mentioned above?
A: OSFP 400G DACs & AOCs are possible for breakout 400G connections. See 400G Direct Attach Cables (DAC & AOC) Overview for more information about 400G DACs & AOCs.
Original Source: 400G OSFP Transceiver Types Overview

