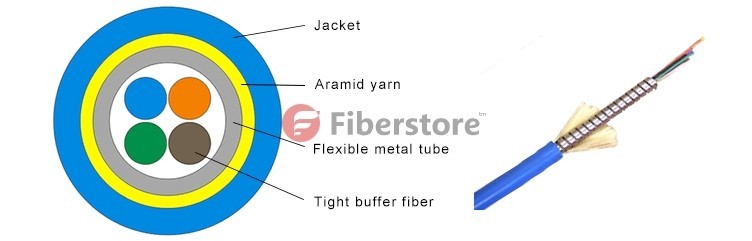
Wire enclosed in metal sheathing is called armored cable (AC). It is sometimes called by its trade name, BX. Inside the flexible metal sheathing are insulated hot and neutral (grounded) wires and a bare bonding wire. BX is restricted to use indoors in dry locations. It is rarely used in new construction (except in high-rise building) because it is expensive and difficult to install. Nevertheless, it is often found in older homes. It divided into outdoor fiber cable and Indoor fiber cable. Metal-clad cable (MC) is a more common type of armored fiber cable. The two fiber optical cables look alike but are easy to tell apart if you know what to look for. MC cable includes a green grounding wire while AC cable does not. The metal covering on MC cable is not permitted to be the grounding conductor. The wires in MC cable are wrapped in a plastic tape to protect them from chatting against the armored sheathing. Be sure to insert a plastic sleeve between the wires and the armor wherever wires emerge from the armored fiber cable.
For BX, different fittings are used to attach the cable to electrical boxes. All BX fitting work the same way the cable goes through center of the fitting. The armor itself is connected within the fitting and is held in place by one or two clamps or a twist-on mechanism. As stated, BX is not easy to work with. To splice one BX cable into another requires cutting the armor sheathing without harming the wires inside. This can only be done using a hacksaw or a specialized tool that cuts any type of armored fiber optic cable. The tool just barely cuts through the armor, which is then twisted to break cleanly, exposing the wires inside. Another drawback to BX is that it cannot turn a tight radius because of the metal sheathing. Too tight a turn radius because of the metal sheathing. Too tight a turn will kink the armor, creating a sharp edge. Sharp edges are also created wherever armored fiber cable is cut. This is why it is so important to always install a protective sleeve on the cut ends of the cable to protect the wires inside. The following picture is an example of single-armored multi-core indoor cable
Armored covers give the cable an additional breaking durability and protect it from crushing. Sparse or dense metal braids, ribbons of corrugated steel, or round steel wires of various diameters serve as the armor.
There are two kinds of armor made from steel ribbon some tenths of a millimeter thick. Most frequently its seam runs parallel to the axis of the cable. In this case, the ribbon necessarily has small corrugation that allow high flexibility of the cable. Armor made by the winding of a steel ribbon (in this case the axes of the ribbon and the cable core are located at a certain angle) is rarely used. In the second case, a surface of the ribbon is made smooth, which somewhat reduces the second case, a surface of the ribbon is made smooth, which somewhat reduces the cable external diameter. The ribbon surface in modern design is frequently covered with a polymeric corrosion-resistant material.
Armor made from steel wires of various diameters is used in poor conditions and significant tensile loads may occur. If is necessary, two layers of wire may be applied on the cable with the axes of the wires positioned at low angles to the cable axis, but with different winding layers. Wire braid armor with wire diameters of some tenths of a millimeter substantially differs from the steel corrugated ribbon by its smaller overall diameter and greater flexibility, however, because of the low efficiency of wire-wrapping machines, it is rarely used.
The primary armored covers are frequently supplemented with braids of glass fiber reinforced plastic threads; sometimes the ribbon armor is additionally strengthened by two or four steel wires intruded into the material of the external jacket (this design is used, for example, by Lucent Technologies and Siemens). The latter ensures cable-stretching stability close to that of cables with common wore armor, with only slight increases in the weight and external diameter of the cable. We note that according to the information from some cable manufacturers (in particular, Siemens) only layers of round steel wire are considered as the armored covers of cables. Other strengthening components refer to elements to protect against rodents.
The role of the armor is then to improve the mechanical resistance of the cable by increasing its rigidity. The function of such armor is complex. sing-armored cable, and with a view to controlling the elongation of the conductor. Double armor, the underlying layer of steel-based bands, resistance to external attack and other subjects such as the cable’s behavior on the seabed, are not discussed here. There are specialized works available that may be consulted which deal with these issues in detail.
Fiberstore is a famous fiber optic cable shop, it has different types of fiber optic cables, at the same time there is a good news I have to tell you, Fiberstore is doing with 30% of the price about the fiber optic cables and other related devices, it you want to know more information, take action for it. http://www.fs.com/