As an essential part in the whole optic communication system, fiber optic transceiver is a device that transforms electrical signal into optical signals so that the information could transmit in the optical fiber. Once getting to the destination, the transceiver then transforms optical signals into electrical signal. Since it is a conversion device, transceiver must be put on the corresponding equipment so that it can be used.
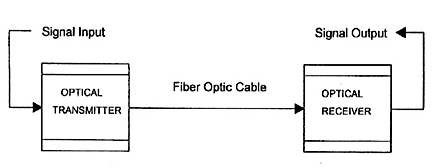
Fiber optic transceiver is an optoelectronic device made up of functional circuit and optical interface, aiming at transforming electrical signals into optical signals. It is used for transforming signals between the switches and devices. The optoelectronic functional circuit includes two parts: the transmitter and the receiver. First the transmitter converts the electrical signals into optical signals and transforms the signals to the receiver, usually through the optical fiber cable. The transmitting part is responsible for inputting a certain rate of electrical signals by internal driver chip to drive the semiconductor laser or LED (light emitting diode) to emit the corresponding rate of optical signal modulation. Inside the transceiver, there is an automatic control circuit, which could ensure a stable optical signal power. The receiving part is in charge of inputting a certain rate of optical signals and then transforming it into electrical signals by LD (laser diodes), at last outputting the corresponding electrical signals through the preamplifier.
According to different standards, fiber optic transceiver can be divided into different kinds. In general, it can be classified by its package, transmission rate, and function (with or without hot pluggable). Among them, the most common classification is the first one, by its package.
- GBIC transceiver module: Gigabit Bitrate Interface Convert, a hot pluggable device, has been widely used before the SFP was developed. But now it is nearly knocked out besides being used on some outdated facilities.
- SFP transceiver module: Short for Small Form-factor Pluggable, it is an enhanced version of early GBIC, but smaller size than GBIC. The common optic module is often referred to as this one.
- XFP transceiver module: 10 Gigabit Small Form-factor Pluggable, It is used on 10Gbps SONET / SDH, Fibre Channel, 10 Gigabit Ethernet. XFP has a higher transmission rate and transmitting capacity, but also a higher price than common transceiver modules.
- XENPAK transceiver module: With a 10.3G working rate and a XAUI interface, XENPAK is a hot-pluggable device which is compliance with XENPAK MSA protocol and it can meet the demand of 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GbE) standard.
- X2 transceiver module: A hot pluggable in the Z-direction module that is usable in typical router line card applications, Storage, IP network and LAN (Local Area Network) and compliant to XENPAK MSA. It is designed for 10Gbps applications.
- 100Base transceiver module: transmission rate 155 Mb/s
- 1000Base transceiver module: transmission rate 1.25 Gb/s
- 2.5G transceiver module: transmission rate 2.5 Gb/s
- 4.25G transceiver module: transmission rate 4.25 Gb/s
- 6G transceiver module: transmission rate 6 Gb/s
- 8.5G transceiver module: transmission rate 8.5 Gb/s
- 10G transceiver module: transmission rate 10 Gb/s
- 40G transceiver module: transmission rate 40 Gb/s
- 100G transceiver module: transmission rate 100 Gb/s
Fiber optic transceivers can fall into two categories: hot pluggable transceivers and non pluggable transceivers. The former one means the users don’t need to shut down the system or cut off the power if they want to replace the damaged parts, so that it could improve recovery ability and flexibility of the system. While non pluggable device could cause permanent damage if it is forced to take out. Fiber optic transceivers has two kinds in this classification: hot pluggable and non pluggable. The latter is much more popular among users.
In conclusion, without a fiber optic transceiver, the whole optical communication system could not orderly operated. It is a device used to send and receive information, including two parts: a transmitter and a receiver. It has two ends, one that an optical cable plugs into and another for connecting an electrical device. According to its different packages, different transmission rate, hot pluggable or non pluggable, we can fall them into different categories.
If you are looking for a fiber optic transceiver, Fiberstore is a good choice. There are a number of different types of fiber optic transceivers available, which are used for a variety of applications both in home and industrial fields. They differ in the types as well as in the quality of data transmission and the speed may change from device to device. Go and search your targeted transceiver in Fiberstore!