Ethernet patch cable has already become a ubiquitous part of our everyday experience. It is generally used for connecting virtually all networking components, providing a flexible and cost-effective way of transmitting voice, data, and multimedia over integrated networks. When dealing with Ethernet patch cables, we sometimes get confused regarding patch cable wiring schemes and when they should be employed. So this article will try to shed some light on this commonly confused subject.
Since the wiring scheme of different Ethernet patch cable varies, we’ d better get to know the categories of it as well as its wiring standard. Basically, Ethernet patch cable comes in two types: straight-through cables and crossover cables. As for the wiring standard, there existing T568A and T568B defined in the ANSI/TIA-568-C.2 standard for 4-pair (8-position, 8-conductor) RJ45 interfaces. When used in traditional fashion, there is no functional difference between patch cords with T568A or T568B wiring standards. Both wiring standards are acceptable and are essentially interchangeable. The only difference between T568A and T568B specification is the orientation of the green and orange wire pairs.
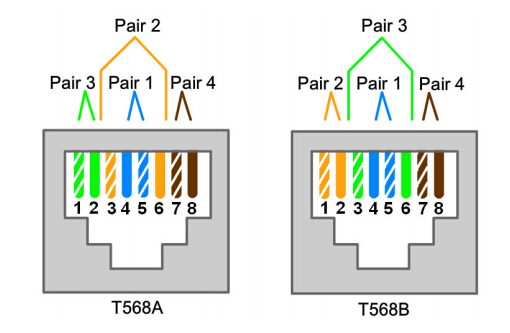
In the previous part, we have mentioned the common types of Ethernet patch cables. So next we will further explain their features and illustrate the wiring scheme of each in details.
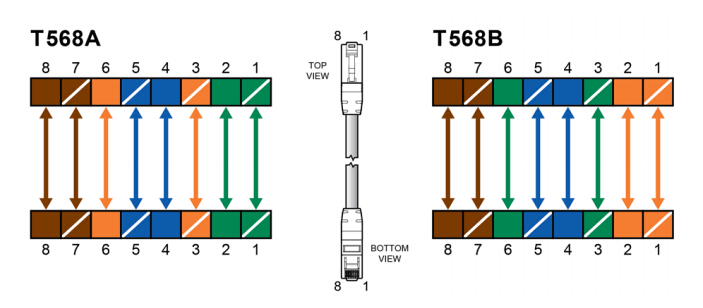
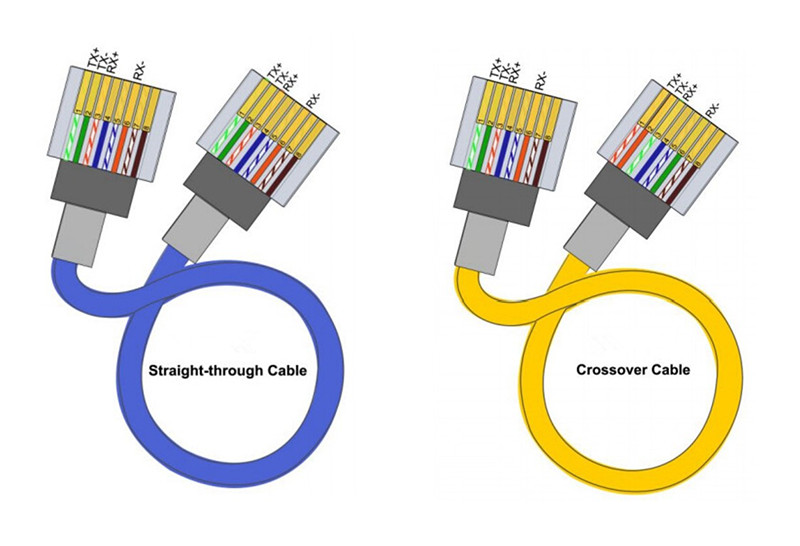
Straight-Through cables get its name due to the fact that both of its ends are configured in the same way. This kind of Ethernet patch cable often adopts the same wiring standard: either T568A or T568B layout. Which means out of the 8 pins on both ends of an Ethernet cable, each pin connects to the same pin on the opposite side. Most Ethernet patch cables on the market are straight-through cables, and they are typically used to connect unlike devices, such as connecting a router to a hub, a computer to a switch and a LAN port to a switch, hub or computer.
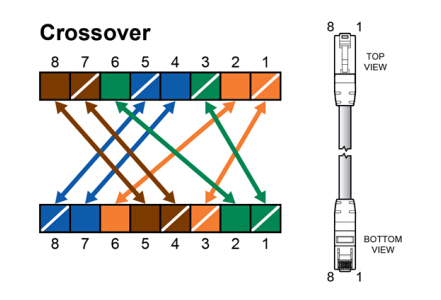
Judging from the physical appearance, crossover cables just resemble that of the straight-through cables. However, the difference actually lies in the order that the wires are arranged: the send and receive pairs in this cable are crossed from one module plug to the other. Crossover cables use two different wiring standards: one end uses T568A wiring standard, while the other applies T568B wiring standard. This Ethernet patch cable is preferred for direct connection between the same devices: a PC to another PC, a hub to hub or switch to switch.
Knowing the difference between the two types of Ethernet patch cables is proved to be useful, especially when connecting them to various components. Let’ s see how to efficiently identify each.
The easiest way to tell what kind of Ethernet patch cable you have is to look at both of its ends together. If both cable ends are configured according to the T568A or T568B standard for both connector ends, then the cable is a straight-through patch cord. But if the patch cable is wired according to the T568A standard at one end, and the T568B at the other end, the cable is a crossover cable. Crossover cables sometimes have orange or yellow sheaths to make them easier to identify.
Ethernet patch cable facilitates our life in various aspects, and it also has played a significant role in the development of generic and structured cabling system. I hope this article could help to eliminate any confusion with regard to the features and wiring schemes of different Ethernet patch cables. FS.COM offers a wide range of Ethernet cables (Cat5e/Cat6/Cat7) and accessories. For more information and tutorials, visit www.fs.com.