Power over Ethernet technology, also referred to as PoE, enables people to adopt the Ethernet cable to transmit data to the PoE device while supply power at the same time, thus reducing the use of power lines and saving costs. PoE technology is very commonly used in IP camera, wireless AP etc. PoE switch, especially 48 Port PoE Switch, has been widely deployed in many enterprise networks, this article will introduce it in details.
Basics of PoE Network Switch
PoE switch is a device that is used to transmits data signal and provides power for IP-based terminal devices (such as IP phones, wireless APs, IP cameras, etc.) on the basis of existing Ethernet cabling, it usually configures multiple Ethernet ports, supports output power up of 15.4W or 30W and complies with IEEE802.3af/802.3at standard, eliminates the need for additional power cabling since power is supplied to standard PoE terminal equipment via network cable. PoE Switch may come in different ports with different speed. The 48 port gigabit PoE switch has been commonly seen in many networks.
Application Instance of PoE Network Switch
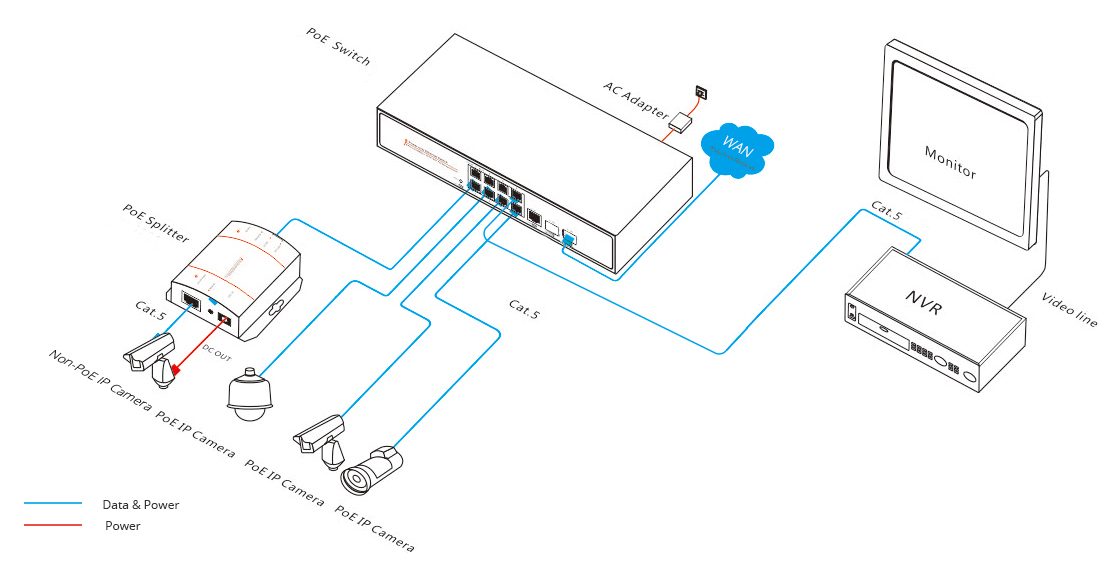
The use of PoE switch eliminates the process of IP terminal equipment cabling, the overall network comes to be more reliable, and makes the deployment if IP terminal devices become more flexible without reply on direct power. The figure below is an example of a PoE switch used to monitor the system, a PoE switch can supply power for multiple IP cameras that is very convenient to deploy. For a 48 Port PoE Switch, that means 48 IP cameras can get power from this PoE network switch without the extra need to find a location for a power outlet.
Is a POE Network Switch Worth It?
To add a 24 or 48 port PoE Switch isn’t incredibly expensive, nor is it more difficult than other switches to be handled. Nowadays, many devices are compatible with PoE switch. A PoE network switch can help save both time and money for network deployment and maintenance. As the technology advances and matures, it can be predicted that PoE network switch will gain a larger market share in the future.
Related Article: Deploying 48-Port Gigabit PoE Managed Switch in Different Networks