40G bandwidths are now being widely adopted within LANs and Data Centres. And 100G will soon be required within your local networks. Here comes the question: what type of fibre network you should choose when planning your 40/100 GbE migration. You have to consider your cabling infrastructure and how it will meet your current and future data requirements. The cables of choice for data center connectivity and what is recommended by the TIA are OM3 and OM4 laser-optimized multimode fiber. In this post, a comparison between OM3 and OM4 fibers will be given.
The IEEE 802.3ba 40/100G Ethernet Standard was ratified in June 2010 and specified parallel optics transmission for multimode fiber. OM3 and OM4 are the only multimode fibers included in the standard. OM3 and OM4 laser-optimized 50/125µm multimode fibers are the choice fiber type for connectivity in the data center. The fibers provide a significant value proposition when compared to single-mode fiber, as multimode fiber utilizes low cost 850 nm transceivers for serial and parallel transmission. Below we look at the differences between OM3 and OM4 multi-mode fibers. The picture shows laser-optimized multimode fiber cables.

OM3 is fully compatible with OM4. The connectors are the same, the termination of the connectors is the same, the fibre core size 50/125 is the same, and both fibers are laser optimised multi-mode fiber (LOMMF). The difference is just in the construction of the fibre cable. The difference in the construction means that OM4 cable has better attenuation and can operate at higher bandwidth than OM3.
Attenuation: Attenuation is the reduction in power of the light signal as it is transmitted. It is caused by losses in light through the passive components, such as cables, cable splices, and connectors. The difference in OM3 and OM4 performance is in the loss (dB) in the cable. OM4 causes lower losses.
Dispersion: Dispersion is the spreading of the signal in time due to the differing paths the light can take down the fiber. Modal dispersion, which means that the spreading of the signal in time resulting from the different propagation modes in the fiber. OM3 specifies an effective modal bandwidth (EMB) of 2000 MHz/km, and OM4 of 4700 MHz/km, showing that OM4 can operate at higher bandwidth.
The cost for OM4 is greater due to the manufacture process and economies of scale that the production of OM3 benefits from due to the volumes currently produced. Costs vary depending on the construction type of the cable (loose tube, tight buffered, etc.). OM4 cable is about twice as expensive as OM3 cable. This means that for lots of products such as standard fibre patch panels, MTP cassette modules, fibre patch cords the cost difference is very small (as the volume of cable is small).
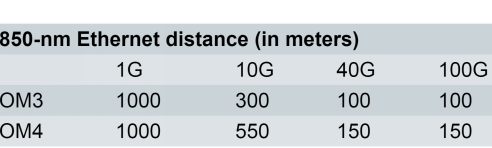
OM4 effectively provides an additional layer of performance that supports these applications at longer distances, as shown in the following picture. OM4 provides an opportunity to future-proof cabling infrastructure, for it can provide a minimum reach of 125m over multimode fiber within the 40 and 100 GbE standards. Additionally, OM4 provides additional reach at extended bandwidth at an overall cost still less than that of an OS2 singlemode system. In other words, OM4 provides a solution that allows more installations to avoid the significantly higher costs of singlemode systems.
It is important to note that OM4 glass is not necessarily designed to be a replacement for OM3. Despite the relatively long-standing availability of OM4, there are no plans to obsolete OM3 fiber optic cabling. Fiberstore offers you a wide range of cable choices for your 40G Ethernet applications, like OM3 and OM4 fiber optic patch cables. And we also offer other 40G components, such as QSFP+ transceiver, copper cable, active optical cable and QSFP+ cable. You can buy from us with confidence.
